Uncategorised
Birds in Mt Wilson
Ducks and swans
Australasian darter
Herons and egrets
White-necked heron
Ibises and spoonbills
Straw-necked ibis
Masked lapwing
Eagles, kites and goshawks
Brown goshawk
Grey goshawk
Wedge-tailed eagle
Pigeons and doves
White-headed pigeon
Brown cuckoo dove
Common bronzewing
Brush bronzewing
Crested pigeon
Bar-shouldered dove
Wonga pigeon
Cockatoos
Yellow-tailed black cockatoo
Gang-gang cockatoo
Parrots and lorikeets
Galah
Rainbow lorikeet
Australian king parrot
Crimson rosella
Eastern rosella
Cuckoos
Fan-tailed cuckoo
Shining bronze-cuckoo
Horsfield’s bronze-cuckoo
Channel-billed cuckoo
Owls
Powerful owl
Southern boobook
Sooty owl
Eastern barn owl
Frogmouths and nightjars
Tawny frogmouth
Kingfishers
Azure kingfisher
Laughing kookaburra
Superb lyrebird
Treecreepers
White-throated treecreeper
Red-browed treecreeper
Fairy-wrens
Superb fairy-wren
Variegated fairy-wren
Pardalotes
Spotted pardalote
Scrubwrens, thornbills and gerygones
Pilotbird
Rockwarbler
Yellow-throated scrubwren
White-browed scrubwren
Large-billed scrubwren
Brown gerygone
Brown thornbill
Striated thornbill
Honeyeaters
Red wattlebird
Little wattlebird
Bell miner
Lewin’s honeyeater
Yellow-faced honeyeater
White-eared honeyeater
White-naped honeyeater
Crescent honeyeater
New Holland honeyeater
Tawny-crowned honeyeater
Eastern spinebill
Jacky winter
Australian robins
Scarlet robin
Red-capped robin
Flame robin
Rose robin
Eastern yellow robin
Eastern whipbird
Whistlers and allies
Golden whistler
Grey shrike-thrush
Crested shrike-tit
Black-faced monarch
Fantails
Grey fantail
Rufous fantail
Willie wagtail
Cuckoo-shrikes
Black-faced cuckoo-shrike
Currawongs and allies
Grey butcherbird
Pied butcherbird
Pied currawong
Grey currawong
Australian magpie
Ravens and crows
Australian raven
White-winged chough
Satin bowerbird
Finches
Red-browed finch
Mistletoebird
Swallows and martins
Welcome swallow
Tree martin
Fairy martin
Songlarks
Rufous songlark
Brown songlark
Silvereye
Bassian thrush
Introduced birds
Red-whiskered bulbul
Common blackbird
Common starling
Blackberry (Rubus fruticosus agg spp)
Declared a noxious weed.
A native of Europe. Blackberry is an erect scrambling perennial shrub with long arching thorny canes which grow up to 2-3 metres (6ft-10ft) in height and are deciduous on Mount Wilson and Mount Irvine. The many white flowers are followed by berries which are green, turning red then black as they ripen in February and March.
The berries which contain the seeds are spread by birds all over the Mountain and quickly form new plants in ideal conditions. The canes will also grow by suckering, so a large dense prickly bush will soon form.
A combined effort by landowners and the Council is now needed annually to control Blackberry on some private land where it is a big problem, causing continual reinfestation of the reserves and roadsides.
Control
- Dig out small plants.
- Spray fruiting plants November to January, non-fruiting plants up to March.
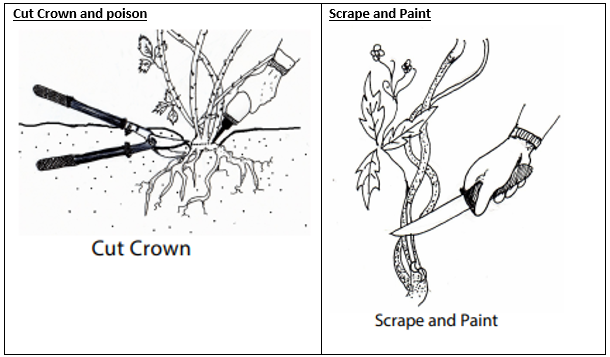
- Cut crown and poison: For mature plants with a woody crown (root ball) – the cut crown method is very effective. It involves removing soil from the base of the plant where it's coming from the ground and cutting through the crown at the widest point to create maximum surface area to apply herbicide.
- Scrap and Paint: For all other plants - seedlings, juvenile and mature without accessible root crown, scrape and paint canes. Paint every stem for 300mm (8in- 12in) of its length
Herbicides
- Spray - Tree and Blackberry killer
- Paint - Tree and Blackberry killer or Glyphosphate (Roundup)
Please note special care must be taken when using herbicides and especially Glyphosate. The MWPA accepts no responsibility for the use or application of any chemicals. Always check the labels and Safety Data Sheets for all chemicals and use only as directed. For more details on herbicides refer to the additional information sources below.
Useful Sources of Information:
Common Holly (Ilex Aquifolium)
After English Ivy, Common Holly is the most ubiquitous weed in Mt Wilson.
There are many old established Holly Trees and hedges in Mt Wilson. Whilst owners may be reluctant to remove these, care should be taken to stop the spread of Holly trees. Holly gets established very quickly and it is easiest to remove when the plants are still small. When they are seedlings they can sometimes be dug up as long as all roots are removed. Holly cuttings should all be placed in the green bin, mulched or burnt as they reshoot very easily.
The extract below is from Libby Raines weed booklet.
A native of Europe to China and North Africa. Holly is a large fast growing evergreen shrub (a small tree on Mount Wilson). It has very prickly shining green leaves and many red berries in the Autumn, which are carried by the birds. Each berry contains up to four seeds, which germinate readily in our ideal conditions, especially in the shade, and they quickly make a large self-layering shrub which usually shades out everything else around it.
Holly can be seen almost everywhere you walk on good soil. Holly and Ivy are the two most serious weeds on Mount Wilson. It is heartening to see many land owners removing holly trees from their properties.
The variegated forms of Holly are suitable to grow.
Control
- Pull or dig out small plants or spray December to March.
- Large plants cut off and poison.
Resources
Current Bushfire Status
Update about the Gospers Mountain Fire to the north of us, posted Wednesday, 11 December.
Gospers Mountain Bushfire Update - Plan to begin backburning today.

The Gospers Mountain bushfire seen yesterday from Smiths Hill was about 6 kms from Mount Irvine
The Fire
While we have a good weather window MWMIRFS Brigade will commence back burning into the area below Mount Irvine today to take advantage of the better conditions for creating a safety burnt area around Mt Irvine. This will involve lighting the bush from the fire trails around Mount Irvine then Mount Wilson to remove the fuel between the villages and the Gospers Mountain fire thereby protecting property in the villages. The back burn is a lower intensity burn usually lit at night and going downhill so as to reduce the impact on the surrounding bush while removing the fuel and protecting the area from the bushfire coming into the villages on a bad day.
On Tuesday the fire was holding on Bungleboori Creek (see yesterday’s Update map), north of Mt Wilson / Mt Irvine, but quite active on the Newnes Plateau. The back burn started at Mountain Lagoon has progressed as far as Bilpin. After a very hot day yesterday we are entering a good weather window until about Friday.
Access to the Mounts
A road block at Mt Wilson Road and the Bells Line of Road will restrict access to all vehicles other than residents and emergency services. Expect this to be in place for a couple of weeks.
Letters of authority were distributed last night to all residents providing access to named people on the presentation of the letter and ID like a local rates’ notice or a driver’s licence. If you need an authority for anyone else (other than Mount Wilson or Mount Irvine residents) please email to This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it. stating: first name, family name and email address. A personalised authority letter will be sent to the nominated person.
The trigger point for fire plans
The start of backburning is the trigger point for people to carry out their fire plans. If you plan to leave, today is the time to relocate. Leave, stay or come to the Mounts this is also the time to contact your Street Coordinator and tell them what you will be doing. A fire warning message may be sent to all mobile phones in the area when fire reaches a preset zone around both villages . Do not be alarmed by this, just follow the prompts and check with your street coordinator if the situation or conditions may have changed.
Once backburning starts we will see an increase of smoke in the area. From today expect increased movement of trucks, activity around both community halls and fire stations and road closures in areas as the backburn progress from Mount Irvine to Mount Wilson and on along Mt Wilson Road to Bells Line of Road.
Please slow down on the local roads, if possible pull over and let tucks pass. Do not enter the fire trails or the burn area as there will be many hazards, machinery operating, steep trails, falling trees and hot ash beds.
Anyone who would like to assist with Catering or Station work please contact the Brigade Station Officer on 4756 2168.
Peter Raines
Senior Deputy Captain
Mt Wilson-Mt Irvine RF Brigade
Map of Fires in NSW with the current status of each fire, Fires Near Me.
The map can be zoomed to show fires in our area.
